On this page
- What are diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
- What are the symptoms of diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
- What are the complications of diverticulitis?
- What causes diverticular disease?
- How is diverticular disease diagnosed?
- How is diverticular disease treated?
- When is surgery necessary for diverticulitis?
- Points to Remember
What are diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
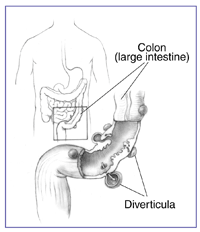
Diverticula are most common in the lower portion of the large intestine, called the sigmoid colon. When the pouches become inflamed, the condition is called diverticulitis. Ten to 25 percent of people with diverticulosis get diverticulitis. (3) Diverticulosis and diverticulitis together are called diverticular disease.
(1) Bogardus ST. What do we know about diverticular disease? A brief overview. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. 2006;40:S108–S111. (2) Ibid. (3) Ibid.
What are the symptoms of diverticulosis and diverticulitis?
Diverticulosis
Most people with diverticulosis do not have any discomfort or symptoms. However, some people may experience crampy pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, bloating, and constipation. Other conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome and stomach ulcers cause similar problems, so the symptoms do not always mean a person has diverticulosis. People with chronic symptoms should visit their doctor or health care provider.
Diverticulitis
The most common symptom of diverticulitis is abdominal pain. The most common sign on examination is tenderness in the lower left side of the abdomen. Usually, the pain is severe and comes on suddenly, but it can also be mild and become worse over several days. The intensity of the pain can fluctuate. A person may experience cramping, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, or a change in bowel habits.
What are the complications of diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis can lead to bleeding; infections; small tears, called perforations; or blockages in the colon. These complications always require treatment to prevent them from progressing and causing serious illness.
Bleeding
Rectal bleeding from diverticula is a rare complication. Doctors believe the bleeding is caused by a small blood vessel in a diverticulum that weakens and then bursts. When diverticula bleed, blood may appear in the toilet or in the stool. Bleeding can be severe. A person who has bleeding from the rectum—even a small amount—should see a doctor right away. Often, colonoscopy is used to identify the site of bleeding and stop the bleeding. Sometimes the doctor injects dye into an artery—a procedure called angiography—to identify and treat diverticular bleeding. If the bleeding does not stop, surgery may be necessary to remove the involved portion of the colon.
Abscess, Perforation, and Peritonitis
Diverticulitis may lead to infection, which often clears up after a few days of treatment with antibiotics. If the infection gets worse, an abscess may form in the wall of the colon.
An abscess is a localized collection of pus that may cause swelling and destroy tissue. If the abscess is small and remains in the wall of the colon, it may clear up after treatment with antibiotics. If the abscess does not clear up with antibiotics, the doctor may need to drain it using a catheter—a small tube—placed into the abscess through the skin. After giving the patient numbing medicine, the doctor inserts the needle through the skin until reaching the abscess and then drains the fluid through the catheter. This process may be guided by sonography or x ray.
Infected diverticula may develop perforations. Sometimes the perforations leak pus out of the colon and form a large abscess in the abdominal cavity, a condition called peritonitis. A person with peritonitis may be extremely ill with nausea, vomiting, fever, and severe abdominal tenderness. The condition requires immediate surgery to clean the abdominal cavity and remove the damaged part of the colon. Without prompt treatment, peritonitis can be fatal.
Fistula
A fistula is an abnormal connection of tissue between two organs or between an organ and the skin. Fistulas typically occur because severe inflammation destroys the space between two structures. The organs that occasionally fistualize with the colon during a severe case of diverticulitis include the bladder, small intestine, and skin. Some fistulas close on their own over time. Most require surgery.
Intestinal Obstruction
Scarring caused by diverticulitis may lead to partial or total blockage of the intestine, called intestinal obstruction. When the intestine is blocked, the colon is unable to move bowel contents normally. If the intestine is completely blocked, emergency surgery is necessary. Partial blockage is not an emergency, so the surgery to correct it can be planned.
What causes diverticular disease?
Although not proven, the dominant theory is that a low-fiber diet causes diverticular disease. The disease was first noticed in the United States in the early 1900s, around the time processed foods were introduced into the American diet. Consumption of processed foods greatly reduced Americans’ fiber intake.
Diverticular disease is common in developed or industrialized countries—particularly the United States, England, and Australia—where low-fiber diets are consumed. The disease is rare in Asia and Africa, where most people eat high-fiber diets.
Fiber is the part of fruits, vegetables, and grains that the body cannot digest. Some fiber, called soluble fiber, dissolves easily in water. It takes on a soft, jelly-like texture in the intestines. Insoluble fiber passes almost unchanged through the intestines. Both kinds of fiber help prevent constipation by making stools soft and easy to pass.
Lack of exercise also may be associated with a greater risk of forming diverticula, although the reasons for this are not well understood.
Doctors are not certain what causes diverticula to become inflamed. The inflammation may begin when bacteria or stool are caught in the diverticula. An attack of diverticulitis can develop suddenly and without warning.
How is diverticular disease diagnosed?
Because most people do not have symptoms, diverticulosis is often found through tests ordered for another ailment. For example, diverticulosis is most often found during a colonoscopy done to screen for cancer or polyps.
f diverticulitis is suspected, the doctor may order a computed tomography scan (CT scan or “cat scan”) of the abdomen. A CT scan is a noninvasive x ray that produces cross-section images of the body. The doctor may inject dye into a vein and the person may be given a similar mixture to swallow. The person lies on a table that slides into a donut-shaped machine. The dye helps to show complications of diverticulitis such as perforations and abscesse
How is diverticular disease treated?
A high-fiber diet and pain medications help relieve symptoms in most cases of diverticulosis. Uncomplicated diverticulitis with mild symptoms usually requires the person to rest, take oral antibiotics, and be on a liquid diet for a period of time. Sometimes an attack of diverticulitis is serious enough to require a hospital stay, intravenous (IV) antibiotics, and possibly surgery.
Diverticulosis
Increasing the amount of fiber in the diet may reduce symptoms of diverticulosis and prevent complications such as diverticulitis. Fiber keeps stool soft and lowers pressure inside the colon so that bowel contents can move through easily. The American Dietetic Association recommends consuming 20 to 35 grams of fiber each day.
The doctor may also recommend taking a fiber product such as methylcellulose (Citrucel), psyllium (Metamucil) or wheat dextrin (Benefiber) one to three times a day. These products are available in powder, pills, or wafers, and provide 2 to 3.5 grams of fiber per dose. Fiber products should be taken with at least 8 ounces of water.
Avoidance of nuts, corn, popcorn, and seeds has been recommended by physicians out of fear that food particles could enter, block, or irritate the diverticula. However, no scientific data support this treatment measure. Eating a high-fiber diet is the only requirement highly emphasized across the medical literature. Eliminating specific foods is not necessary. People differ in the amounts and types of foods they can eat. Decisions about diet should be made based on what works best for each person. Keeping a food diary may help identify what foods may cause symptoms.
Diverticulitis
Treatment for diverticulitis focuses on clearing up the inflammation and infection, resting the colon, and preventing or minimizing complications.
Depending on the severity of symptoms, the doctor may recommend rest, oral antibiotics, a pain reliever, and a liquid diet. If symptoms ease after a few days, the doctor will recommend gradually increasing the amount of high-fiber foods in the diet.
Severe cases of diverticulitis with acute pain and complications will likely require a hospital stay. Most cases of severe diverticulitis are treated with IV antibiotics and a few days without food or drink to help the colon rest. In some cases, surgery may be necessary.
When is surgery necessary for diverticulitis?
If symptoms of diverticulitis are frequent the doctor may advise surgery. The surgeon removes the affected part of the colon and joins the remaining sections. This type of surgery—called partial colectomy—aims to prevent complications and future diverticulitis. The doctor may also recommend surgery for complications such as a fistula or partial intestinal obstruction.
Immediate surgery may be necessary when the patient has other complications, such as perforation, a large abscess, peritonitis, complete intestinal obstruction, or severe bleeding. In these cases, two surgeries may be needed because it is not safe to rejoin the colon right away. During the first surgery, the surgeon cleans the infected abdominal cavity, removes the portion of the affected colon, and performs a temporary colostomy, creating an opening, or stoma, in the abdomen. The end of the colon is connected to the opening to allow normal eating while healing occurs. Stool is collected in a pouch attached to the stoma. In the second surgery several months later, the surgeon rejoins the ends of the colon and closes the stoma.
Points to Remember
- Diverticulosis occurs when small pouches called diverticula bulge outward through weak spots in the colon, or large intestine.
- Most people with diverticulosis never have any discomfort or symptoms.
- Diverticula form when pressure builds inside the colon wall, usually because of constipation.
- The most likely cause of diverticulosis is a low-fiber diet because it increases constipation and pressure inside the colon.
- For most people with diverticulosis, eating a high-fiber diet is the only treatment needed.
- Diverticulitis occurs when the pouches become inflamed and cause pain and tenderness in the lower left side of the abdomen.
- Diverticulitis can lead to bleeding; infections; small tears, called perforations; or blockages in the colon. These complications always require treatment to prevent them from progressing and causing serious illness.
- Severe cases of diverticulitis with acute pain and complications will likely require a hospital stay. When a person has complications or does not respond to medication, surgery may be necessary.

